Vitamins for Wound Repair: The Power of Vitamins Enhancing Wound Healing Through Nutrition
To repair skin effectively, the body needs a variety of essential nutrients. These include the building blocks like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, as well as vital micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. Working together, these nutrients coordinate the complex process of wound healing.
Content table
Vitamins are involved in the wound healing process by supporting cellular functions, boosting immune responses, and promoting the synthesis of key proteins like collagen. Without adequate vitamin intake, the body’s ability to repair and regenerate damaged tissue is compromised, leading to delayed healing and increased risk of complications.
Some of the vitamins involved in the wound healing process include vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin K, each with its unique function that together orchestrate a seamless repair mechanism.
Understanding the importance of these vitamins can help optimize your diet and improve your body’s natural healing capabilities. Let’s explore the specific roles and benefits of each of these essential vitamins in wound healing.
What are vitamins?
Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for various physiological functions in the body. They are required in small amounts and cannot be synthesized by the body in sufficient quantities, so they must be obtained through the diet.
Each vitamin has a unique role in maintaining health, supporting metabolism, and facilitating biochemical reactions necessary for growth, development, and overall well-being.
Vitamins are typically divided into two categories:
Fat-Soluble Vitamins: These vitamins are absorbed along with dietary fats and can be stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. They include:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
Water-Soluble Vitamins: These vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored in the body, so they need to be consumed regularly. They include:
- • Vitamin C
- • B-Vitamins
Why are vitamins so important?
Vitamins are essential for human health because they perform a wide array of vital functions in the body, ensuring that various physiological processes operate smoothly and efficiently. Here’s why vitamins are crucial:
- Energy production
- Immune function
- Antioxidant protection
- Bone health
- Skin health
- Blood clotting
- Neurological function
- Red blood cell formation
- DNA synthesis and cell division
- Wound healing
- Mental health
Key vitamins for wound repair
Some vitamins play a critical role in the wound healing process by supporting various cellular and physiological functions that are necessary for tissue repair and regeneration.
Here’s a detailed look at how specific vitamins contribute to wound healing:
Vitamin A (Retinol)
Enhances Epithelialization: Vitamin A promotes the growth and differentiation of epithelial cells, which are essential for forming new skin over a wound.
Supports Immune Function: It boosts the immune response, helping to prevent infections that can complicate wound healing.
Stimulates Collagen Production: Collagen is a key structural protein in the skin, and vitamin A is involved in its synthesis and organization.
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Collagen Synthesis: Vitamin C is crucial for the production and cross-linking of collagen fibers, providing structural integrity to the wound site.
Antioxidant Protection: It acts as an antioxidant, reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells involved in the healing process from damage.
Enhances Immune Response: Vitamin C supports the function of neutrophils and other white blood cells, aiding in the defense against infection.
Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
Antioxidant Properties: Vitamin E protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, which can impede the healing process.
Skin Health: It may help to reduce scarring and improve skin texture around the wound area.
Vitamin K
Blood Clotting: Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of proteins required for blood clotting, which is the first step in wound healing. Proper clotting helps prevent excessive bleeding and stabilizes the wound site.
Bone Health: It plays a role in bone metabolism and may help heal wounds involving bones.
B Vitamins
Energy Production: Vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6 are involved in metabolic pathways that produce energy, which is crucial for cell proliferation and repair during wound healing.
Red Blood Cell Formation: Folic acid and B12 are essential for the production of red blood cells, which deliver oxygen and nutrients to the healing tissue.
Cell Proliferation and DNA Synthesis: Folic acid and vitamin B12 are critical for DNA synthesis and cell division, both of which are necessary for regenerating new tissue.
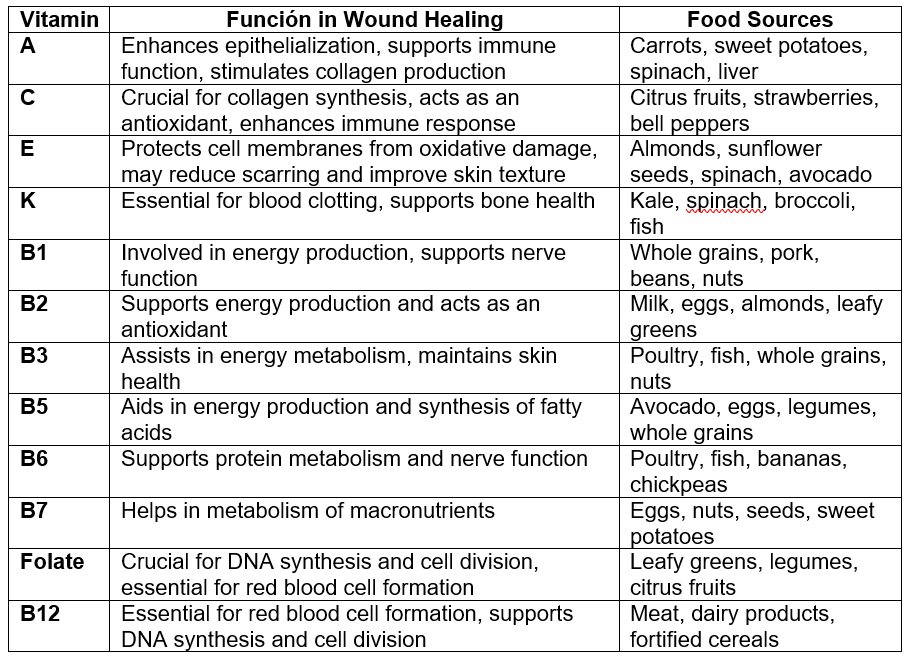
Table 1. Summary of vitamins for wound repair
Synergistic Effects of Vitamins
Combined Antioxidant Defense: Vitamins C and E work together to protect cells from oxidative damage.
Immune Support: Vitamins A, C, and E collectively enhance immune function, reducing the risk of infection at the wound site.
Collagen Formation: Vitamins A and C both contribute to collagen synthesis, strengthening the structural framework of the healing tissue.
Secure your vitamin intake through a healthy diet
Optimizing dietary vitamin intake for enhanced wound healing involves focusing on a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, ensuring adequate consumption of specific vitamins that support the healing process. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
1. Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables daily
Vitamin C: Include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), strawberries, bell peppers, and leafy greens like spinach and kale to boost collagen synthesis and immune function.
Vitamin A: Add orange and yellow vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes) and dark leafy greens (spinach, kale) to promote epithelialization and immune health.
2. Choose protein-rich foods
Vitamin B6: Consume poultry, fish, and legumes to support protein metabolism and repair.
Vitamin B12: Include meats, dairy products, and fortified cereals to aid in red blood cell formation and tissue regeneration.
3. Include nuts and seeds
Vitamin E: Incorporate almonds, sunflower seeds, and avocado to benefit from antioxidant protection and support skin health.
4. Opt for whole grains
B Vitamins: Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and whole wheat are rich in B vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5) that are essential for energy production and cell repair.
5. Get your vitamin K
Include leafy green vegetables, healthy fats such as avocados and fish, and animal products such as liver and eggs. vitamin K and support blood clotting and bone health.
7. Stay hydrated
Adequate hydration supports nutrient transport and overall skin health, enhancing the effectiveness of vitamins in the healing process.
8. Consider supplements if necessary
If dietary intake is insufficient, consider vitamin supplements, particularly if you have specific deficiencies or increased needs. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
9. Avoid nutrient depletion
Limit alcohol consumption and avoid excessive use of medications that can deplete vitamin levels, as these can interfere with the healing process.
Supplementation can be a valuable tool in optimizing wound healing, especially when dietary intake alone is insufficient or when specific needs arise due to health conditions or lifestyle factors. Here are some of the reasons or scenarios in which supplementation might be needed:
Deficiencies
If blood tests reveal deficiencies in specific vitamins (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin D, or B vitamins), supplementation can help address these gaps and support the healing process.
Signs such as delayed wound healing, frequent infections, or poor skin health may indicate a need for additional vitamins.
Inadequate Dietary Intake
Individuals on restrictive diets (e.g., vegan, vegetarian) may not get sufficient amounts of certain vitamins like B12 or vitamin D from their food and may need supplements.
In cases of reduced appetite or eating disorders, it might be challenging to consume adequate nutrients through food alone.
Severe or complex wounds
Vitamin supplementation may be necessary for increased physiological needs, such as in cases of severe or chronic wounds like pressure ulcers, diabetic ulcers, severe burns, or large wounds that require more nutrients for healing. Additionally, patients recovering from surgery often need extra vitamins to support tissue repair and regeneration.
Malabsorption Issues
Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or other gastrointestinal disorders that affect nutrient absorption might necessitate vitamin supplementation.
Older adults may also experience reduced absorption of nutrients, leading to a need for supplements to support wound healing.
Medications and Interactions
Certain medications can deplete vitamin levels or interfere with their absorption. In such cases, supplements might be needed to counteract these effects.
Supplements may be required if you are taking medications that affect vitamin levels or nutrient utilization.
Immune Support
For individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatment, specific vitamin supplements can enhance immune function and support wound healing.
Guidelines for Supplementation
-Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any vitamin supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your specific situation and to determine the correct dosage.
-Choose high-quality supplements from reputable sources to ensure efficacy and safety.
-Regularly assess the effectiveness of supplementation and adjust as necessary based on feedback from your healthcare provider.
Takeaways
- Specific vitamins like A, C, E, K, and B vitamins play essential roles in the wound healing process by supporting collagen synthesis, immune function, blood clotting, and cell proliferation.
- Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins, ensures you receive the necessary vitamins for wound healing.
- Adequate water intake is crucial for nutrient transport and overall skin health, enhancing the effectiveness of vitamins in the healing process.
- In cases of diagnosed deficiencies, restrictive diets, increased needs, or malabsorption issues, vitamin supplementation might be required to ensure adequate intake for optimal wound healing.
- Before starting any vitamin supplements, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the need, appropriate dosage, and monitor progress to avoid potential interactions or side effects.